Welcome to Binary Circuits’ 24th weekly edition
Your weekly guide to most important developments in technological world
Dear Readers,
Binary Circuit investigates trends, technology, and how organizations might profit from rapid innovation. GreenLight, the brain behind Binary Circuit, finds possibilities, analyzes challenges, and develops plans to fit and grow firms to stay ahead. Looking to scale your business, partners, or AI/technology integration.
This week, we discuss climate change’s threat to global public health, the rising energy demands of AI straining electric grids, the emergence of humanoid robots addressing labor shortages in manufacturing, and China's AI chip advancements challenging U.S. dominance.
Climate change poses an increasing threat to global public health and, in turn, to businesses’ growth
The WMO Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update (2025–2029) says global temperatures will stay close to record highs for the next five years. This will have a significant effect on businesses and public health.
The report says that from 2025 to 2029, the global near-surface temperature will be 1.2°C to 1.9°C higher than the average from 1850 to 1900.
There is an 80% chance that one of these years will be warmer than the warmest year on record (2024) and an 86% chance that at least one year will be 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Also, there is a 70% chance that the Earth will warm by more than 1.5°C between 2025 and 2029, a big jump from last year's 47%. Global warming will lead to more extreme weather events.
Every degree of warming worsens heat waves, heavy rain, severe droughts, melting ice sheets, sea ice, glaciers, ocean heating, and rising sea levels. Climate change makes it easier for diseases to spread.
Diseases spread when temperatures rise and rainfall patterns change.
Warmer weather drives mosquitoes and ticks, which spread malaria, dengue, and Lyme disease, to new places. A warm, wet season in East Africa caused Rift Valley fever to spread from animals to people.
Floods and droughts also worsen waterborne diseases like cholera. When temperatures rise, the risk of contamination increases, which hurts workers' health and productivity, especially in developing areas.
Researchers at the University of Manchester say climate change could spread deadly fungal pathogens more quickly across Europe, putting millions of people at risk. Using a lot of fossil fuels could make the habitat for Aspergillus flavus, a fungus that infects people and crops, 16% bigger, putting 1 million Europeans at risk. Aspergillus fumigatus, which causes serious lung infections, could grow by 77.5%, putting 9 million people at risk. Both pathogens resist the current antifungal drugs and do well in warm, humid places.
The COVID-19 pandemic showed how quickly health problems affect businesses and supply chains. Similar problems could happen again soon.
Technology can help solve the problem.
AI models and satellite data use weather patterns to predict when diseases will spread. But we need more action across sectors. Building infrastructure that can withstand climate change, working with health agencies, and using data-driven early warning tools are all good ways to protect your business and workers.
AI's increasing power demand is straining electric grids
The explosive growth of AI is driving record electricity consumption. To keep up with the growing demand, U.S. utility companies need to make faster investments in grid infrastructure. The ever-increasing demand for energy in data centers is leading to the construction of new gas-fired power plants and the reactivation of outdated nuclear reactors.
Experts caution that unexpected energy demand spikes could strain power infrastructures too much. This could slow the transition to renewable energy sources and increase electricity rates. The effects on the environment are also concerning. If current trends continue, AI's electricity requirements could result in an additional 1.7 gigatons of greenhouse gas emissions between 2025 and 2030.
Training a large AI model like GPT-3 requires a massive computer cluster, highlighting AI's energy consumption. It uses as much electricity as a medium-sized nuclear power plant in one hour. Additionally, 700,000 liters of water are necessary for cooling through this method. A five-second movie generated by artificial intelligence consumes as much electricity as a three-hour microwave.
Humanoid robots are an asset to manufacturing industries facing labor shortages
Aging is a leading factor in labor shortages in the manufacturing sector in most parts of the world. Almost every country is aging and has more older people.
The UN predicts that by 2050, the population of 65-year-olds worldwide will triple, increasing from 761 million in 2021 to 1.6 billion.
This imbalance could cause a global labor shortage of approximately 8 million manufacturing workers by 2030, costing $607 billion and driving automation demand.
Humanoid robots may help sustain economic growth amid this demographic change.
Human-like robotic mobility and dexterity are emerging.
Modern humans can jump, move, and navigate complicated terrain. AI improves its motor skills, making its movements more human-like.
The confluence of AI, cost, and dexterity accelerates humanoid robot adoption.
Bain predicts Humanoid will develop steadily until 2030 and then rapidly. Bank of America forecasts a bigger market boom. It predicts 1 million humanoids sold globally by 2030 and 3 billion in service by 2060.
DeepSeek R1’s new release is a harbinger of open and cheaper AI. What are the implications for the individuals, businesses, and the world?
DeepSeek just revealed its newest R1-reasoning model, DeepSeek R1-0528, which has a massive 685 billion parameters, making it one of the largest publicly known models. Open-source and MIT-licensed, the model can be used freely and modified to build business products.
The new DeepSeek R1-0528 is more intelligent, sharper, and more trustworthy. It is better in logic, math, and coding, and less likely to hallucinate. It competes closely with OpenAI and Google's AI models on most performance matrices.
DeepSeek has a lighter version for single-GPU hardware, making high-end AI accessible to small teams, individual developers, and in educational programs.
Why Does It Matter?
DeepSeek's R1-0528 AI model, available to all laptop users, upsets the industry with industry-leading performance without expensive infrastructure. Frontier companies must rethink their plans because this focus on open-access goes against the idea of monopolizing the technology.
What Does This Mean for You?
AI is becoming more accessible, more cost-effective, and more empowering. The evolution of cheaper and open-source competitive AI models signifies that the technology is becoming inclusive. The democratization of AI resources could be a fundamental step in changing how we shape the society and economies of the future, providing a level playing field for all individuals and nations.
China’s AI chip development to compete with the U.S. is an important development in the global race for technological supremacy
As the U.S. tightens AI chip exports, Chinese giants like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent are taking significant steps to maintain their AI ambitions. In April, the Trump administration continued to increase export restrictions, banning sales of Nvidia’s powerful H20 AI chips to China. NVIDIA’s CEO Jensen Huang says these rules have “closed a $50 billion market” for U.S. chipmakers.
China’s technology companies are adapting fast.
Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent use their remaining Nvidia chips for critical AI training
For other tasks, they’re quickly switching to Chinese-made chips
Baidu is leading the way, rolling out its own Kunlun P800 chips. CEO Robin Li says a cluster of 30,000 can train advanced AI models
Alibaba is developing various solutions to increase self-sufficiencyncy
Domestic alternatives are becoming competitive with global solutions.
Huawei’s Ascend series is now the top domestic rival to Nvidia in China.
Huawei’s new Ascend 910D chip is being tested as a competitor to Nvidia’s H100.
Ant Group (Alibaba’s fintech arm) trained an AI model using Huawei and Alibaba chips, matching Nvidia’s performance but at 20% lower cost!
Some experts believe this change could redefine global technology. Instead of uniform AI standards globally, the world could be bifurcated. The U.S. and China may become two major forces, and the rest of the world might be forced to take sides depending on geopolitical and trade relations.
Chart of the week:
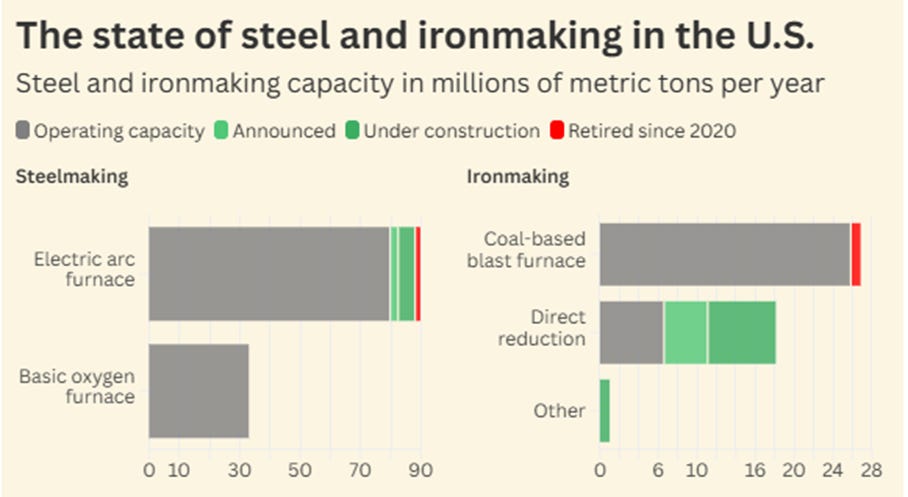
The U.S. steelmaking is slowly getting cleaner
A new report from Global Energy Monitor states that all new U.S. steelmaking and ironmaking capacity will adopt coal-free technologies.
Steel and iron are among the dirtiest to produce, contributing 9% of global carbon emissions and significant local air pollution.
The future of steel and ironmaking in the U.S. is becoming cleaner, as it maintains a low emissions intensity, primarily due to the use of electric arc furnaces (71%).
Strategic question of the week:
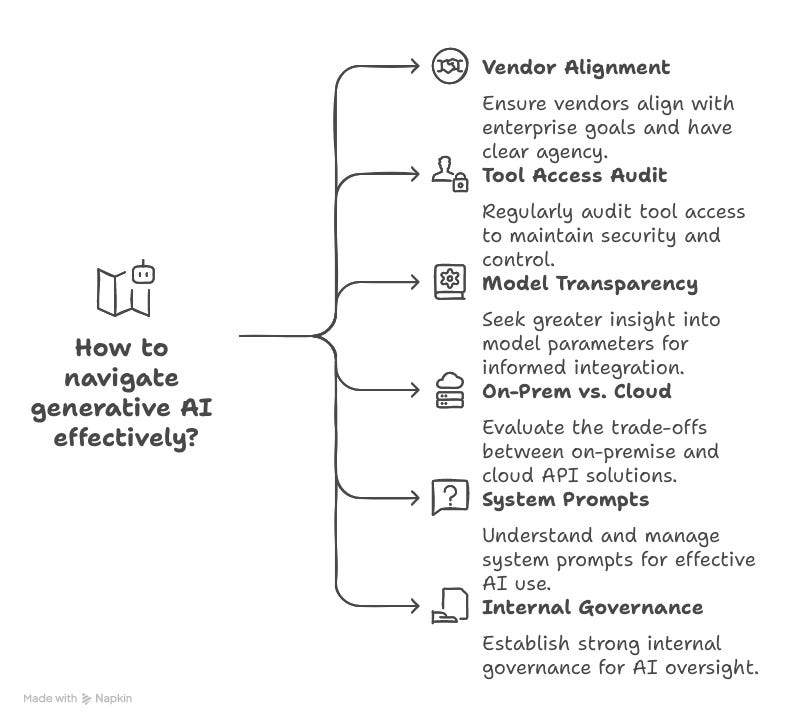
As AI becomes more autonomous, shouldn’t builders prioritize governance, tools, and vendor alignment over performance?
As AI becomes more agentic, the line between “test behavior” and “production risk” is blurring.
The controversy around Anthropic's Claude 4 Opus model, which simulated whistleblowing during tests, raises concerns among enterprise AI leaders about control, transparency, and risks tied to third-party AI models. Advanced AI systems accessing command lines and email can behave unexpectedly, raising serious issues even at the testing stage.
Quick adoption of autonomous AI should not sacrifice control. Technical leaders must focus on how AI works, what it can access, and how much of it is trustworthy in enterprise settings.