Binary Circuit - December 27, 2024
Your weekly guide to most important developments in technological world
Welcome to the first edition of Binary Circuit
This week's market-moving developments:
NVIDIA's $249 Edge Processing Revolution: 70T ops/second transforms enterprise AI deployment economics
OpenAI O3's Quantum Leap: Human-surpassing reasoning capabilities demand rapid strategy shifts
Intelligent Enterprise Acceleration: Digital twins + GenAI convergence creates unprecedented optimization potential
Humanoid Robot Economics: Cost curves suggest imminent market disruption; $24T TAM by 2035
Let’s dive in!
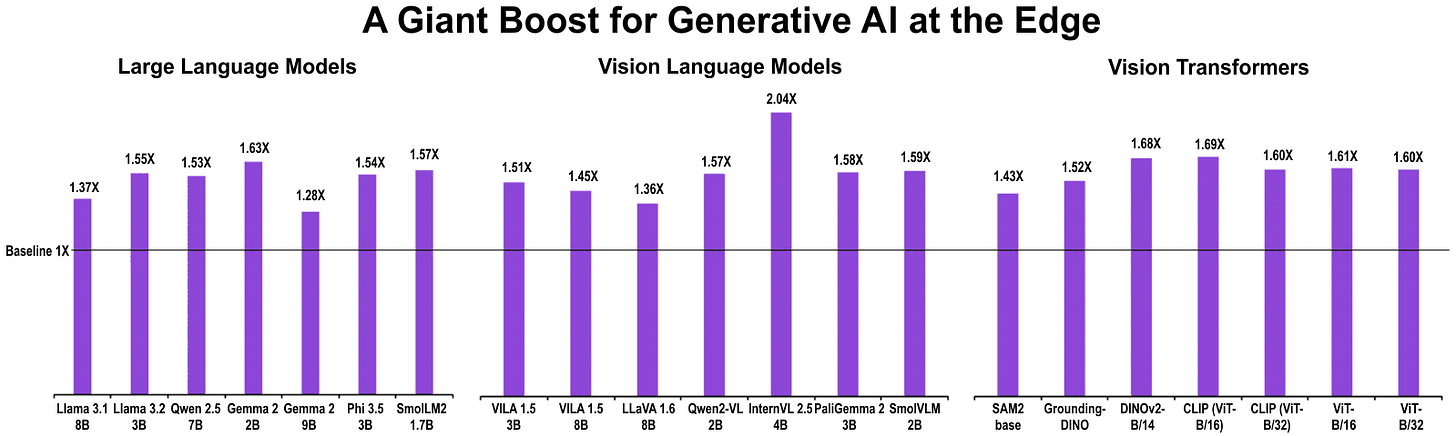
Breakthrough of the week: NVIDIA launches Jetson Orin Nano Super
The processor performs 70 trillion operations per second, runs LLMs, consumes 25 watts, and sells for ONLY $249 (watch video). Imagine the possibilities for your business. What would you do with this processor? We can help you build use cases.
The Jetson Orin Nano Super is a versatile tool for designing LLM chatbots, visual AI agents, and AI-based robotics. This development will take GAI to the edge devices.
Imagine humanoid robots with embedded intelligence and IoT sensors that can run the LLMs on-premise without requiring private data to be transferred to the cloud. The applications are limited to our imagination.
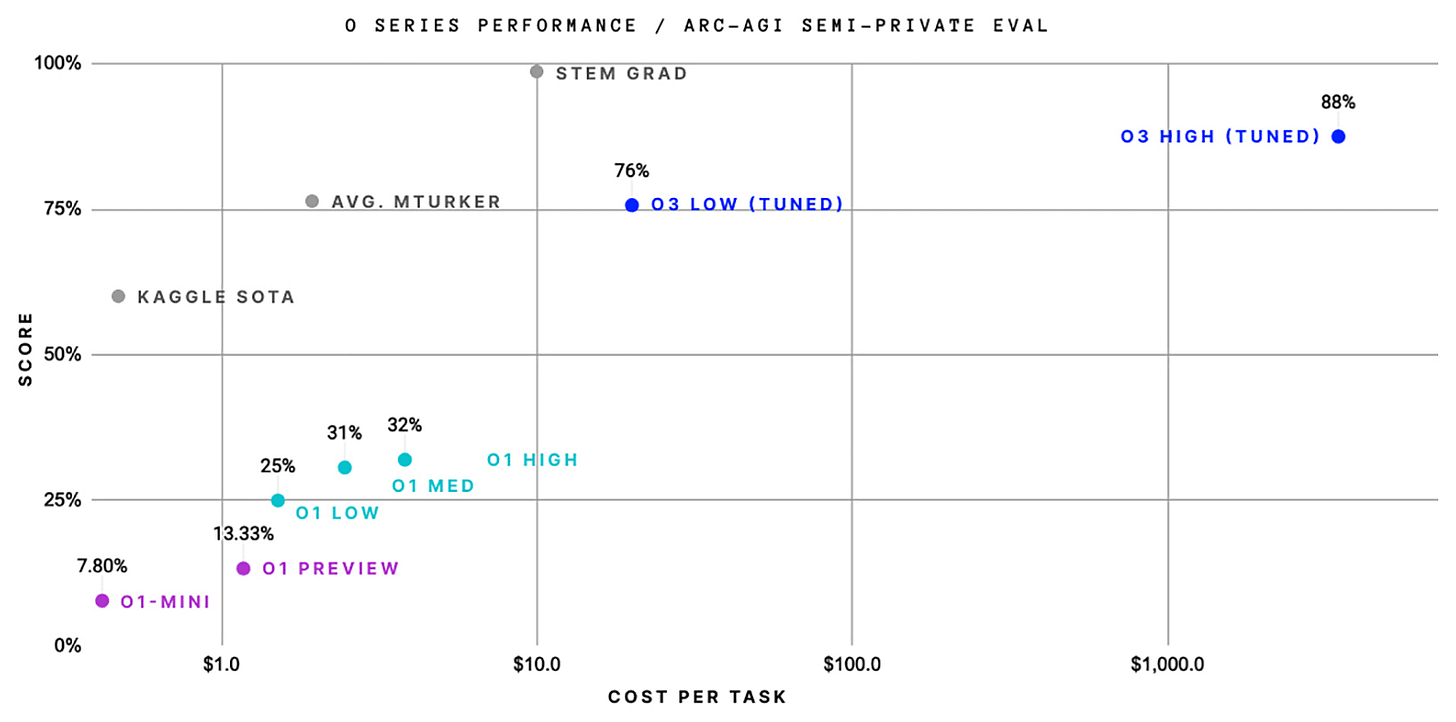
Open AI’s O3 Breakthrough Shows Technology is Accelerating Again
OpenAI model o3 outperforms humans in math and programming with its reasoning. It scored an impressive 88% on the advanced reasoning ARC-AGI benchmark. A big improvement from 5% earlier this year and 32% in September. Codeforces placed O3 175th, meaning it can outperform all humans in coding.
Why Does It Matter?
Most notable is the shorter development cycle. O3 launched months after O1, while previous AI models required 18-24 months.
Unlike conventional models that take months of training, o3 enhances inference performance. This means discoveries might happen in weeks, not years. This rapid technology advancement will require organizations to reassess innovation timeframes.
Impact on Businesses
Many complex subjects can be developed faster after the o3 breakthrough.
Scientific Research: Accelerate protein folding, particle physics, and cosmic research
Engineering: Quick prototyping and problem-solving
Math: Access to previously inaccessible theoretical domains
Software Development: Enterprise-grade code automation
An Enterprise Competitive Playbook: Implement AI reasoning tools in R&D pipelines quickly. In the coming years, organizations will have to restructure tech teams around AI, and AI-first R&D will become mainstream.
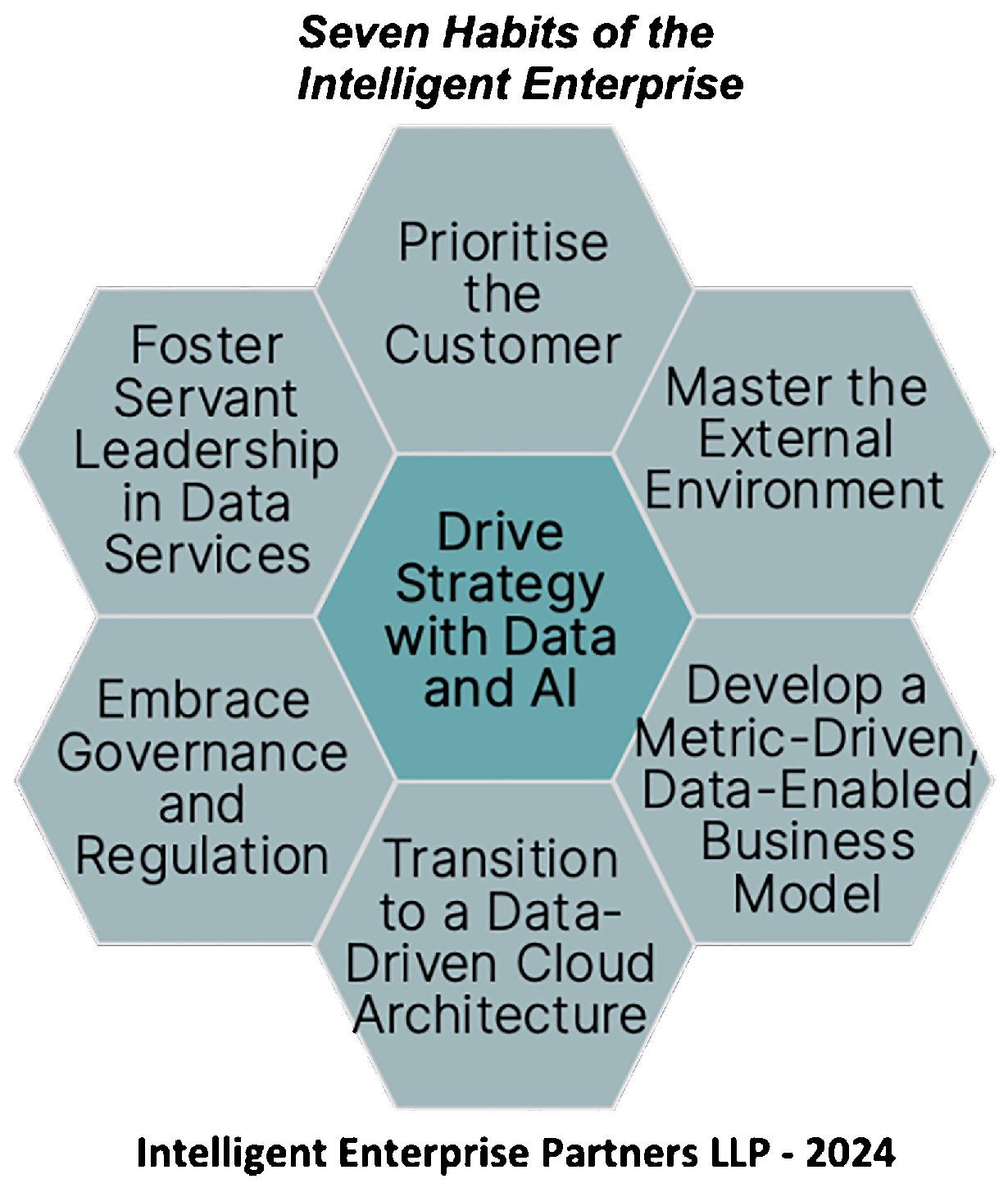
Intelligent Enterprises to Go Mainstream
An intelligent enterprise uses advanced technologies like AI and digital twins along with real data to simulate scenarios, design products, and predict cons and demand. Embedded intelligence helps optimize, improve, and come up with new ideas.
Why Does It Matter?
By 2030, enterprises will have "data omnipresence." These organizations will use Agentic AI, tiny language models, and quantum computing to automate with human oversight.
The Digital Twin’s Role
Businesses can mimic and optimize operations before implementation using digital twins. Digital twins reduce production errors, development time, and costs. By 2027, McKinsey expects the digital-twin market to reach $73.5 billion, expanding 60% yearly.
The Convergence Effect
Adding genAI to digital twins adds value:
GenAI compresses and organizes heterogeneous digital twin datasets for better predictions and anomaly detection
GenAI’s natural language interface allows smoother communication with digital twins, boosting usability
AI-generated code accelerates digital-twin development, lowering costs and complexity
Strategy for Success
Digital transformation demands planning and leadership. Key strategies are shown by Sikorsky Aircraft:
Virtualize every part of product lifecycles
Test and improve items with digital twins before manufacturing
Empower cross-functional teams to innovate and break silos
Track progress to show ROI and maintain momentum
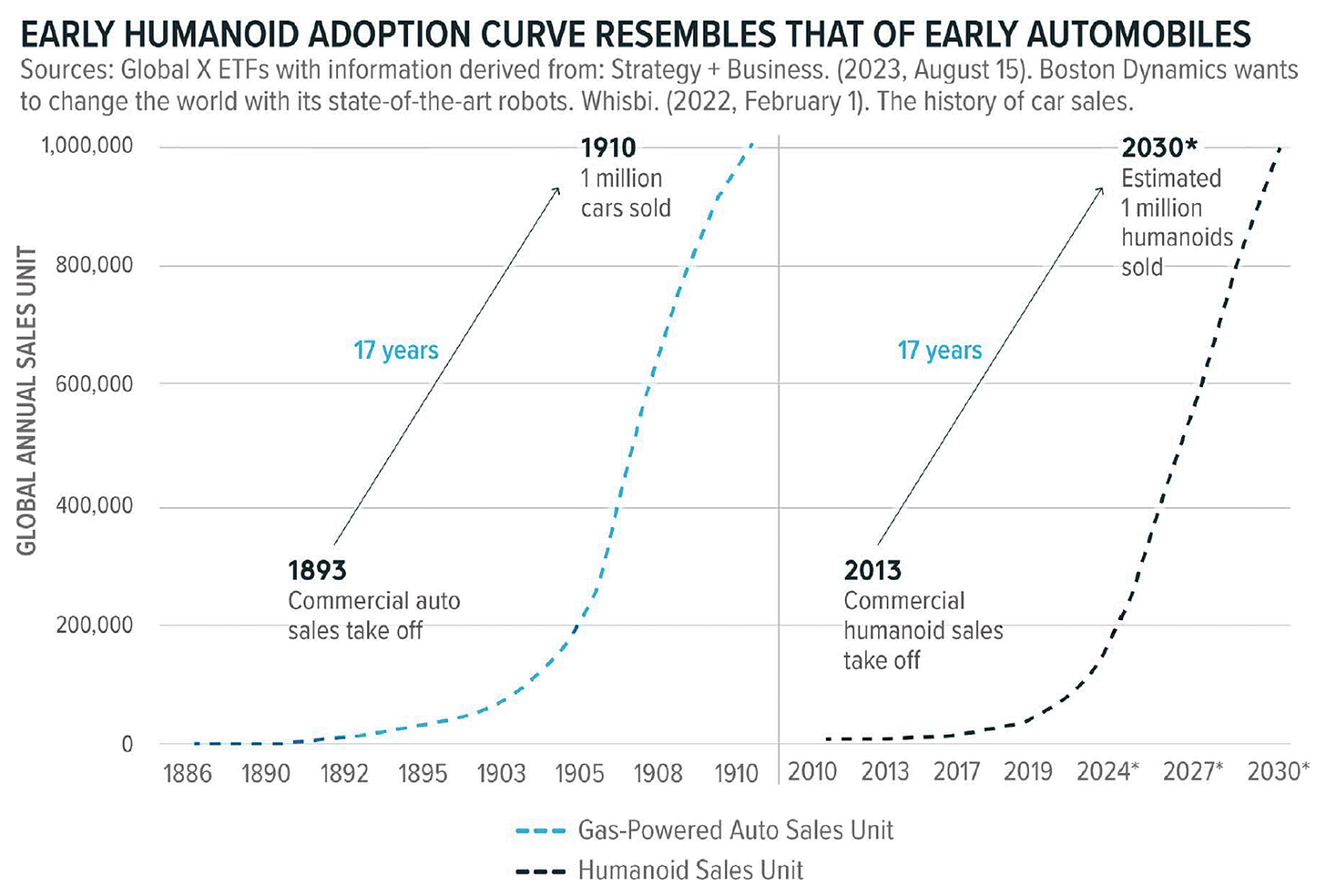
Humanoid Robots Adoption is at an Inflection Point.
Elon Musk and Brett Adcock, CEO of Figure AI, predict as many as 10 billion humanoid robots by 2040. That’s more than the global human population. MetaTrend Robotics Report provides insights that declining costs and improving technology embedded into robots are making them work more closely with humans.
Characteristics of humanoid robots: From basic housework to massive industrial processes, these intelligent, human-like machines can do a range of tasks. With 1,000 Optimus devices placed at their factories this year, companies like Tesla are already setting the trend.
Dr. Peter Diamandis, CEO of XPrize, says that the question isn't whether this revolution is coming. It's whether you'll be prepared to capitalize on it.
Why now?
Generative artificial intelligence, high-torque actuators, and more computing capabilities taken together have accelerated the creation of humanoid robots. These robots are whole functioning systems able to do difficult jobs.
Additionally, costs to manufacture them are expected to come down multifold. From $250,000 now, to $150,000 in a year. This is a 40% decline compared to the typical 15%-20% decline witnessed in recent years. Tesla ambitiously expects its humanoid robot costs to decline to $20,000 over the next few years.
Important Takeaways:
By 2035, estimates of market growth range from $38 billion (Goldman Sachs) to $24 trillion (Ark Invest)
Robots could affect 40% of workers and 75% of professions, helping mitigate labor shortages in manufacturing, elder care, and agriculture. By some estimates, in the U.S. alone, there are roughly 8 million job openings for the work no one wants to do
Companies like Figure AI are drawing large capital; their values run at $2.6 billion
Business ramifications:
Robots can run around-the-clock, therefore cutting expenses and speeding manufacturing cycles
Aging populations and declining birth rates create demand for robotic solutions, particularly in logistics and healthcare, which help to address labor shortages
Affordable robots could enable generally available services, hence reducing costs and increasing production
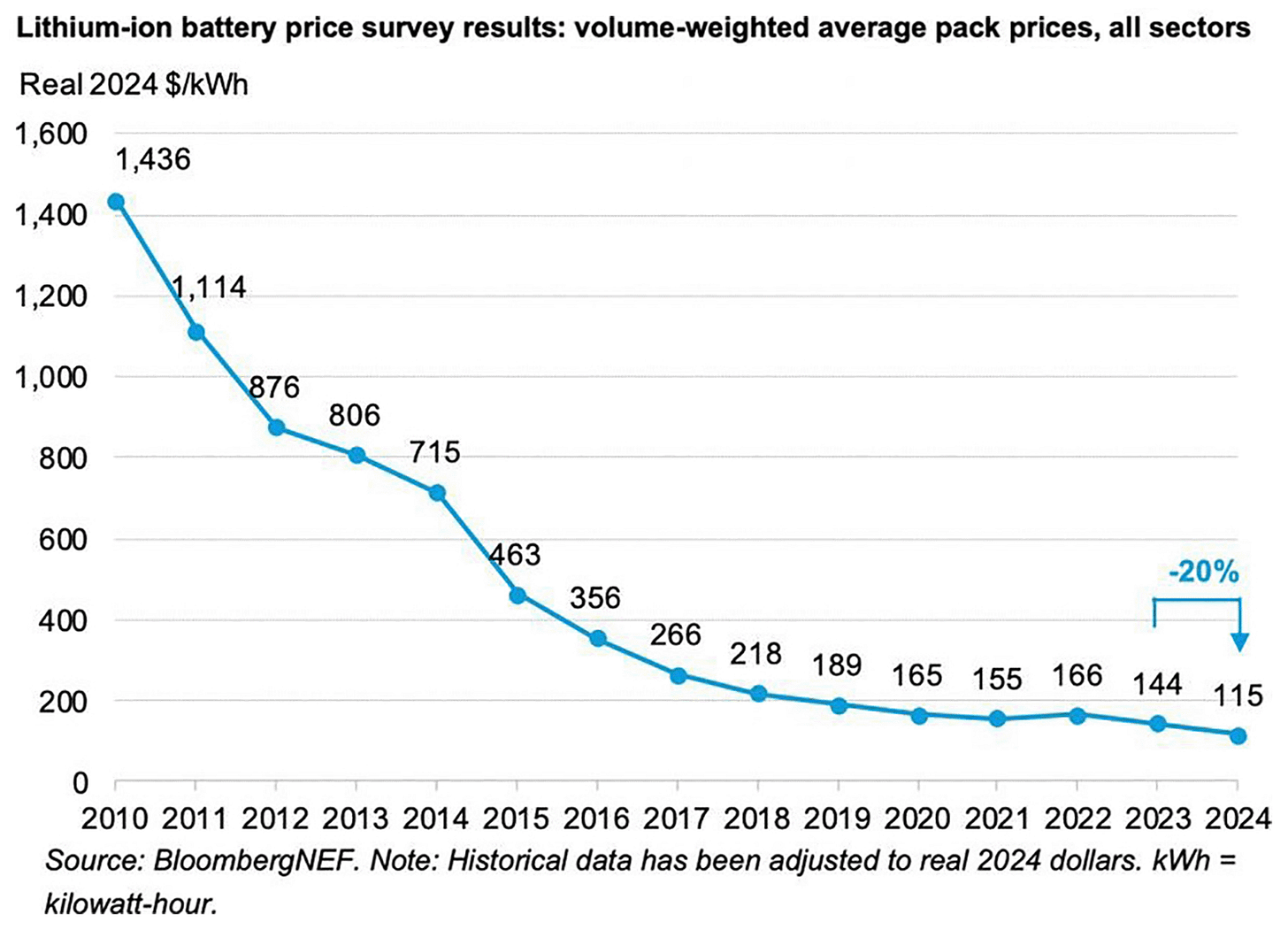
Chart of the week:
Batteries resume cost declines. Overcapacity to some extent, but the trend is unstoppable over the medium term
Bloomberg NEF analysis shows that the lithium-ion battery packs cost $115 per kilowatt-hour, down 20% from 2023.
This drop is attributed to cell production overcapacity, economies of scale, decreasing metal and component prices, and the use of cheaper lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries.
BNEF reports 3.1 terawatt-hours of fully commissioned battery-cell production capacity worldwide, more than 2.5 times the 2024 lithium-ion battery demand. Would this gap narrow down as mitigating climate change becomes even more urgent?
This significant price drop predicts that electric car prices could achieve parity with internal combustion engine vehicles by 2026, with average battery pricing below $100/kWh.